The World in 2024: ten issues that will shape the international agenda

Text finalised on December 15th, 2023. This document is the result of collective reflection on the part of the CIDOB research team.Coordinated and edited by Carme Colomina, it includes contributions from Inés Arco, Anna Ayuso, Ana Ballesteros, Pol Bargués, Moussa Bourekba, Víctor Burguete, Anna Busquets, Javier Carbonell, Carmen Claudín, Francesc Fàbregues, Oriol Farrés, Agustí Fernández de Losada, Marta Galceran, Blanca Garcés, Seán Golden, Berta Güell, Julia Lipscomb, Bet Mañé, Ricardo Martínez, Esther Masclans, Óscar Mateos, Sergio Maydeu, Pol Morillas, Diego Muro, Francesco Pasetti, Héctor Sánchez, Reinhard Schweitzer, Antoni Segura, Cristina Serrano, Eduard Soler i Lecha, Alexandra Vidal and Pere Vilanova.
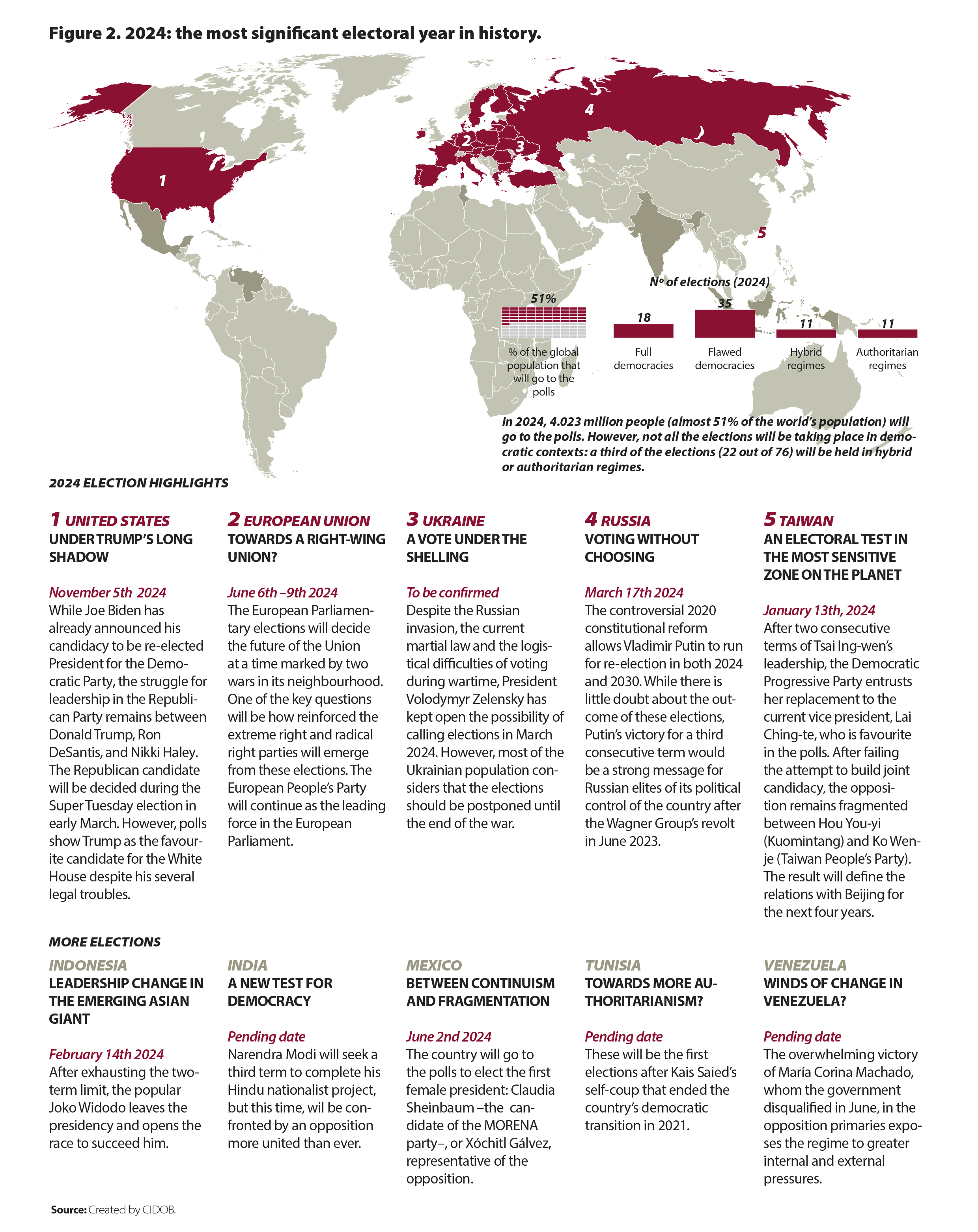
2024 will be a year of ballots and bullets. The elections held in more than 70 countries will serve as a stress test for the democratic system, and the impact of the multiple conflicts stoking global instability will shape a world in the throes of a global power shift and a clear regression in terms of humanitarianism and fundamental rights.
The erosion of international norms is more acute than ever, and events become more unpredictable. 2024 begins wide open, marked by an increasingly diverse and (dis)organised world, with hanging interests and alliances in issues such as geopolitical competition, green and digital transitions, or international security.
The economic consequences of the succession of crises of recent years will be more visible in 2024: economic growth will be weak, and China’s downturn will reverberate in emerging economies, in a climate of rapid tightening of financial conditions and a strong dollar.
2024 will be a year of ballots and bullets, a stress test both for the democratic system and for the multiple conflicts stoking global instability. We still face a world in disarray, in upheaval and in dispute. This time, however, any analysis hangs on the huge question mark of the intense series of elections that will shape the coming year. With all-out hostilities in Ukraine, Palestine, Sudan or Yemen, we are seeing the most active conflicts of any time since the end of the Second World War. How the various armed conflicts and the outcome of the more than 70 elections marked on the calendar impact one another will set the geopolitical agenda for the coming months.
There are elections that can turn the course of a war. The political fallout of the brutal Israeli offensive in Gaza or the stalemate on the Ukraine front also depend on the presidential race in the United States. The cracks in transatlantic unity and the increasingly direct accusations of double standards in the West’s loyalties are not unrelated to what happens in the United States on November 5th, 2024. A return of Donald Trump to the White House would bring a drastic shift in the power relations and Washington’s position in each of these conflicts, from weapons’ supplies to the Ukrainian government or the support for Israel, to confrontation with Russia and China.
Yet it is not only about the future of US democracy; over 4 billion people will go to the polls in more than 70 countries. The European Union (EU), India, Pakistan, Indonesia, Taiwan, Mexico, Venezuela or Senegal, for instance: major actors that wield demographic or geopolitical clout will mark a year of unprecedented electoral intensity and shape a world in the throes of a global power shift and a clear regression in terms of humanitarianism and fundamental rights. More elections do not mean more democracy, however. We live in an age of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and extremely sophisticated manipulation that threatens the integrity of the ballot box. Hybrid systems are gaining ground, and it remains to be seen whether the cycle of elections in 2024 will signal a moment of deep degradation for democracy or a moment of resistance.
The sensation of disorder is not new, nor even its quickening pace. But every year the erosion of current international norms is more marked, and events become more unpredictable. The world is increasingly decentralised, diversified and multidimensional. This “multiplex order”, as Amitav Acharya described it in 2017, is cementing, because everything is happening simultaneously. And yet this reshaping of the world is still wide open because several struggles are playing out at once.

1. More conflict, more impunity
2023 has been one of the most conflictive years in the world since the end of World War II. In just twelve months, political violence has increased by 27%. It grew in intensity and frequency. The war in Gaza brought 2023 to a close, with over 17,000 dead accounted for so far, warnings from the United Nations of the risk of humanitarian collapse and genocide of the Palestinian population trapped in the Strip, and the standoff between the Israeli prime minister, Benjamin Netanyahu, and the UN secretary general, António Guterres, to try to secure a ceasefire. In this ongoing crisis of the liberal order and amid discussion over the validity of international law, Israel has dealt a severe blow to the credibility of the United Nations. The Security Council has become an instrument of paralysis; a pincer in the service of the interests of old powers that have led Guterres to publicly acknowledge his frustration and sense of impotence. A politically weakened United Nations clings to its humanitarian action on the ground to try to make the difference between life and death. At least 130 UN humanitarian workers have lost their lives in Gaza since October 7th, the highest number of UN fatalities in a conflict in its history.
2023 has been a violent year. It is estimated that 1 in 6 people in the world have been exposed to conflict in the last twelve months. The sense of impunity and disregard for international law has escalated. Not only in Gaza. The entrenchment of the war in Ukraine; the expulsion of the ethnic Armenian population from Nagorno Karabakh; or the succession of coups in six African countries in the last 36 months are a clear illustration of this moment of “deregulation of the use of force”, which has been crystallising over years of erosion of international norms. And if in late 2023 we saw the departure of the international troops from the G5 Sahel deployed to Burkina Faso and Niger, as had already occurred the previous year with the expulsion of the French forces from Mali, in 2024 it will be the United Nations mission in Sudan (UNITAMS) that will have to leave the country before February 29th. Human Rights Watch has called the withdrawal a “catastrophic abdication” because it increases the risk of large-scale atrocities and abuses in a scenario of civil war, ethnic cleansing and famine that has forced more than 7 million people to flee their homes, making Sudan the country with the highest number of internally displaced persons in the world.
And yet the international struggle to curtail impunity will be equipped with new tools in 2024. As of January 1st, the Ljubljana - The Hague Convention on International Cooperation in the Investigation and Prosecution of the Crime of Genocide, Crimes against Humanity, War Crimes and other International Crimes could be signed (and ratified) by the United Nations member states that wish to join. It is the primary treaty for fighting impunity for international crimes and facilitates cooperation among states in the judicial investigation of these crimes, it ensures reparation for victims and streamlines extradition. At the same time, the UN is also drafting a Convention on crimes against humanity with the aim of creating a treaty that is binding in international law, especially in a climate marked by an increase in these crimes in countries like Myanmar, Ukraine, Sudan or Ethiopia. The United Nations General Assembly will assess the progress of the negotiations in autumn 2024. It will all coincide with the 30th anniversary of the Rwanda genocide.
In March 2023, the International Criminal Court (ICC) issued an arrest warrant for the Russian president, Vladimir Putin, for war crimes in Ukraine, to no effect so far. But should Putin decide to attend the next G20 summit in Brazil in November 2024, it would present a challenge to the host country since, unlike last year’s host India, Brazil is a party to the Rome Statute of 1998, the international treaty that led to the creation of the ICC. While President Lula da Silva initially said Putin would not be arrested if he attends the summit, he later rowed back, stating that the decision would fall to the Brazilian justice system and not the government.
Despite the pessimism these treaties might produce, in recent months we have seen how, following the Azerbaijani military offensive in Nagorno Karabakh, Armenia signed the ICC’s Rome Statute in November, acquiring member status as of February 2024. In addition, in late 2023 South Africa, Bangladesh, Bolivia, the Comoros and Djibouti called for an International Criminal Court investigation into war crimes, crimes against humanity and genocide in Palestine. In November 2023, the French judicial authorities issued an international arrest warrant for the Syrian president, Bashar al-Assad – rehabilitated back into the Arab League the same year, more than a decade after being thrown out – and for several of his generals over the use of chemical weapons against their own people in 2013.
2. Democracy under scrutiny
More than 4 billion people will go to the polls in 76 countries, which amounts to nearly 51% of the world’s population. While most of the people in these countries will vote in full or flawed democracies, one in four voters will take part in ballots in hybrid and/or authoritarian regimes. In countries such as Russia, Tunisia, Algeria, Belarus, Rwanda or Iran the leaderships will use these elections to try to tighten their grip on power and gain legitimacy in the eyes of their citizens, while the other half of the electorate will exercise their right to vote in countries that have undergone democratic erosion or displayed illiberal tendencies in recent years, like the United States or India.
The close of 2023 saw the inauguration of the “anarcho-capitalist” Javier Milei as Argentina’s president, confirming the deep crisis of traditional parties and the rise of radical agendas, from Nayib Bukele’s aggressively punitive approach in El Salvador ―who will seek re-election in 2024―, to Popular Renewal bursting onto the electoral scene in Peru, following the party’s refoundation by the current mayor of Lima, Rafael López Aliaga. They are extreme responses to the various political, economic and security crisis situations. In Europe, there were mixed results at the polls, with victory for the Polish opposition, on one hand, and a win for the Islamophobic Geert Wilders in the Netherlands, on the other. The rapid succession of elections in 2024 will be decisive in determining whether the protest, fragmentation and rise of political extremism that have transformed democracies worldwide are reinforced or whether the system weathers the storm.
The votes of women and young people will be key in this test of democracy. They were in Poland, punishing the reactionary polices of the Law and Justice Party (PiS). In Brazil or Austria, for example, men’s support of far-right forces is 16 percentage points higher than that of women. In Mexico, the ballot in June 2024 will elect a woman as the country’s president for the first time in its history. The two candidates are Claudia Sheinbaum, a former mayor of the capital, for the ruling leftist party Morena, and Xóchitl Gálvez, for the opposition coalition Broad Front for Mexico, which brings together the conservative National Action Party (PAN) and the PRI (Institutional Revolutionary Party), among others.
In the United States, the mobilisation of young Latinos will be particularly important. More than 4.7 million young Hispanics have obtained the right to vote in the last few years and they will play a significant role in key states like Nevada or Arizona. While this cohort tends to have a progressive stance and leanings, their view of the dominant parties is complex: questions of identity, discrimination or racism colour their relationships with both the Democrats and the Republicans and they reject political identification, reinforcing the idea that polarisation in the United States is more apparent among politicians than among their voters. Despite that, the fear of unfair elections has increased dramatically (from 49% in 2021 to 61% in 2023). Although US voters still perceive economic inequality as the main threat (69%), probably the greatest challenge in this election race is the presence of Donald Trump, not only because his immediate future is in the hands of the courts but also because if he does become the Republican presidential nominee, it will mean that the party has decided to place its future in the hands of the man who tried to overturn the results of the election four years ago and who the Congress committee to investigate the storming of the Capitol on January 6th, 2020, accused of “insurrection”. January will see the start of the state primaries and caucuses. But with the final nominees still to be decided, according to the polls the scenario of an electoral contest between two candidates approaching or in their eighties currently favours Trump. Meanwhile, the date of the former president’s trial can get dangerously close to the Super Tuesday, scheduled for March 5, the day on which 13 states vote in the Republican primaries.
An investigation by The Guardian with the University of Chicago found that 5.5% of Americans, or 14 million people, believe that the use of force is justified to restore Donald Trump to the presidency, while 8.9% of Americans, or 23 million people, believe that force is justified to prevent him from being president. It is not an isolated trend. The risk of political instability and violence related to electoral processes is on the rise, as the Kofi Annan Foundation confirms.
The future of the European Union, which is facing the winter with two wars on its doorstep, will also be decided at the ballot box. Apart from the elections to the European Parliament, which will be held from June 6th to 9th, 2024, 12 member states are also going to the polls. The general elections in Belgium, Portugal or Austria will be a good gauge of the strength of the far right, which is shaping up as one of the winners in the elections to the European Parliament. If the vote in 2019 spelled the end of the grand coalition that had guaranteed social democrats and Christian democrats a majority in the chamber since the European Parliament’s beginnings, the big question now is knowing just how far right the European Union will swing.
The latest voting intention projections show significant results for the Identity and Democracy (ID) group, home of extreme-right parties like Marine Le Pen’s National Rally (RN) and Alternative for Germany (AfD), which would win as many as 87 seats and surpass the other family on the radical right, the European Conservatives and Reformists (ECR), led by the Italian prime minister, Giorgia Meloni, which would go from 66 MEPs at present to 83. Despite the loss of seats for the traditional forces, the European People’s Party (EPP) will remain the EU’s main political family. So, one of the questions in 2024 is whether the EPP, led by the Bavarian Manfred Weber, would be ready to seek a possible majority with the radical right.
The new majorities will be crucial to determining the future of European climate commitments, continued aid to Ukraine and urgent institutional reforms to facilitate the accession of future members. The EU must deliver on the promise of enlargement, but it is increasingly ill-prepared to carry it through.
Four candidate countries to join the EU will hold elections in 2024: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Moldova, North Macedonia, and Georgia, as well as the question mark hanging over the staging of elections in Ukraine. According to its constitution, Ukraine should hold elections in March 2024. But under martial law, imposed in the wake of Russia’s invasion in 2022, with part of the electorate reluctant to vote in such exceptional circumstances and 8 million Ukrainian refugees outside the country, Volodymyr Zelensky already said in November that it was not “the right time” to go to the polls.
The United Kingdom too, in the throes of a political and social crisis could hold early general elections, which are scheduled for January 2025. With the Conservatives facing a challenging scenario against the Labour Party headed by Keir Starmer, the current prime minister, Rishi Sunak, has the power to call the election at a time of his choosing at any point before then. Another issue is Libya. Since the United Nations plan to stage elections was postponed indefinitely in 2021, the inability to reach an agreement between the members of the two governments in the east and west of the country has put the possible date for elections back again, to 2024.
There will be 16 elections in Africa, although only six of them will take place in countries considered to be democratic. Thirty years after the 1994 elections in South Africa, which marked the beginning of a democratic journey dominated since then by the African National Congress (ANC), the political landscape is beginning to change. The 2024 general elections may confirm the weakening of power and support for the ANC, while the main opposition parties seek alliances to present an alternative. In addition, the complicated economic situation, combined with other factors such as corruption, has led to the growing popularity of extremist parties.
Also in India, the opposition presents itself more united than ever against Narendra Modi seeking to renew a third term in the spring. Boosted by nationalism, polarization, and disinformation, Modi will showcase the country’s economic and geopolitical achievements. In 2023 India surpassed China as the most populous country in the world.
Finally, it also remains to be seen what degree of participation the Venezuelan opposition might have in the presidential elections agreed with Nicolás Maduro for the second half of the year. For now, the internal panorama has become even more strained with the intensification of the territorial conflict with Guyana and the mobilization of the army.
3. From information overload to social disconnection
Societies are increasingly weary, overwhelmed by the saturation of content and exhausted by the speed of the changes they must assimilate. Political and electoral uncertainty and the multiple conflicts that will shape 2024 will only widen the distance between society, institutions and political parties.
The number of people who say they “avoid” the news remains close to all-time highs and is particularly prominent in Greece (57%), Bulgaria (57%), Argentina (46%) or the United Kingdom (41%). The main reasons? The excessive repetition of certain news stories and the emotional impact they can have on the population’s mental health. In particular, according to the Reuters Institute, this fatigue is prompted by issues such as the war in Ukraine (39%), national politics (38%) and news related to social justice (31%), with high levels of politicisation and polarisation. The echoes of the COVID-19 pandemic, images of war-related violence and the economic impact of such events on increasingly adverse living standards for the population have magnified this trend towards disconnection, aggravated by a sense of loneliness and polarisation.
Yet this drop in news consumption has gone hand in hand with greater use of social networks: younger generations, for example, are increasingly likely to pay more attention to influencers than to journalists. At the same time, there is growing fragmentation on the social networks. The migration of users to Instagram or TikTok has also changed the way current affairs are consumed, with a prioritisation of leisure over news content.
It is not just a voluntary rejection of information; this tendency to disconnect has also led to a reduction in the social participation and involvement in online debates that had characterised the Arab Springs, the MeToo movement or Black Lives Matter. Nearly half of open social networks users (47%) no longer participate in or react to the news. But, moreover, the disconnect from the news is also linked to the political disconnection and social shifts that have clearly altered electoral behaviour. Demographic changes related to technology use and an environment of constant volatility have also resulted in a drop in voter loyalty and that has contributed to the crisis of the traditional parties. The identity element of belonging to a party has changed among young people. Identification is built on stances on issues such as climate change, immigration, racism, women’s or LGBTQIA+ rights or even the conflict between Israel and Palestine.
Some 65% of American adults say they always or often feel exhausted when thinking about politics. According to the Pew Research Center, six out of ten Americans of voting age admit to having little or no confidence in the future of their country’s political system. And this discontent extends to the three branches of government, the current political leaders and candidates for public office. When asked to sum up their feelings about politics in a word, 79% are negative or critical. The most frequently repeated words are “divisive”, “corrupt”, “chaos” or “polarised”, and they complain that conflicts between Republicans and Democrats receive too much attention and there is too little attention paid “to the important issues facing the country”.
The paradox, however, is that this discontent has coincided with historically high levels of voter turnout over the last few years. The question is whether there will be a repeat of this in the presidential elections in November, especially when they reflect another element of generational disaffection: gerontocracy. The average age of global leaders is 62. In young people’s view, the traditional political parties have failed to articulate a direct form of communication, increasing the sense of disconnection between society, politicians and institutions. In this context, a repeat of the Biden-Trump confrontation in 2024 would emphasize the extreme polarization between Republicans and Democrats in an electoral cycle considered risky. Abortion rights and security remain strong mobilization points for voters.
Sometimes, however, the disconnection can be forced and in this case a news blackout becomes a weapon of repression and censorship or freedom of expression. Iran, India and Pakistan were the three countries with most new internet restrictions in the first half of 2023, and all three are holding elections in 2024. With the rise and consolidation of AI, disinformation will be an additional challenge in this “super election year”. The rapid progress of AI, particularly generative AI, may cast an even longer shadow over trust in information and electoral processes. The refinement of deepfakes, quick and easy creation of images, text, audios files or propaganda by AI and a growing dependence on social media to check and research facts form a breeding ground for disinformation at time when there is still no effective control of these technologies. Perhaps that is why the Merriam-Webster dictionary’s word of the year for 2023 is “authentic”. With the prelude of “post-truth” in 2016, technology’s capacity to manipulate facts has no precedent, from the authenticity of an image to the writing of an academic work. Hence more than half of social media users (56%) say they doubt their own capacity to identify the difference between what is real and fake in news on the internet.
4. Artificial intelligence: explosion and regulation
2023 was the year that generative AI burst into our lives; the year that ChatGPT was presented to society, which in January, just two months after its launch, already had 100 million users. In August, it hit 180 million. Yet the revolution also brought a new awareness of the risks, acceleration and transformation involved in a technology that aspires to match, or even improve or surpass human intelligence. That is why 2024 will be a crucial year for AI regulation. The foundations have already been laid. It only remains to review the different initiatives under way. The most ambitious is that of the European Union, which is resolved to become the first region in the world to equip itself with a comprehensive law to regulate artificial intelligence and lead the coming leap forward. The EU has opted to categorise the risks (unacceptable, high, limited or minimal) posed by the use of AI systems and will require a “fundamental rights impact assessment” be carried out before a “high-risk” AI system can be put on the market. The agreement reached in December will be ratified in the first quarter of 2024 and give way to a period of two years before its full implementation in 2026.
Almost at the eleventh hour too, on December 1st of 2023 the G7 agreed international guidelines for artificial intelligence developers and users, particularly for generative AI, mentioning the need to introduce measures to deal with disinformation. G7 leaders see it as one of the chief risks because of possible manipulation of public opinion on the eve of a year of global election overdrive.
But the debate on governance goes hand in hand with a geopolitical race to lead technological innovation and, unlike the EU, in the case of the United States and China that also means development of its military application. Both countries are looking to bolster their leadership. The first international AI safety summit, called by the British prime minister, Rishi Sunak, became a meeting point of major global powers – both public and private; techno-authoritarian or open – trying to regulate or influence the debates on regulation under way. A second in-person summit will take place in Seoul and a third one in Paris, both in 2024 . For now, the “Bletchley Declaration” is on the table, a document signed by 28 countries that gathers the pledge to tackle the main risks of artificial intelligence, an agreement to examine tech companies’ AI models before they are launched and a deal to assemble a global panel of experts on artificial intelligence inspired by the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel of Experts on Climate Change (IPCC) . In addition, at the US Embassy in London, 31 countries signed a parallel (non-binding) agreement to place limits on the military use of AI. China, for its part, continues to move towards its goal of reaching 70% self-sufficiency in critical technologies by 2025, while clearly increasing its presence in the main tech-related international standardisation bodies.
To add to this flurry of regulatory activity, a Global Digital Compact will be agreed at the Summit of the Future in September 2024, organised by the United Nations. This agreement will create a framework of multi-actor and multisectoral cooperation among governments, private enterprise and civil society, which should lay down a set of common rules to guide digital development in the future. The application of human rights online, the regulation of AI and digital inclusion will be some of the main topics under discussion.
This need to regulate artificial intelligence will also be heightened in the coming months by a growing democratisation of AI tools, which will bring greater integration into different professional sectors. The focus on a responsible AI will be stepped up locally (more cities deploying AI strategies or regulatory frameworks), nationally and transnationally. As AI takes on a more important role in decision-making throughout society safety, trustworthiness, equity and responsibility are crucial. The latest annual McKinsey report on the use of generative AI tools says that a third of companies surveyed had begun to use these types of programs. The tech and communications sector (40%), as well as financial services (38%) and the legal profession (36%), are the frontrunners in their use and application. Yet the same survey also states that precisely the industries relying most heavily on the knowledge of their employees are those that will see a more disruptive impact of these technologies. Whether that impact is positive or negative is still unclear. Unlike other revolutions that had an effect on the labour market, it is white-collar workers who are likely to feel most vulnerable in the face of generative AI. A European Central Bank study, meanwhile, says that AI has not supplanted workers, but it has lowered their wages slightly, especially in jobs considered low and medium-skilled, which are more exposed to automatisation, and particularly among women.
In the midst of this regulatory acceleration of the digital revolution, 2024 will also be the year when the European Union deploys, to it full potential, the new legislation on digital services and markets to place limits and obligations on the monopolistic power of the major platforms and their responsibility in the algorithmic spread of disinformation and harmful content. As of January 1st, it will be compulsory for Big Tech to abide by these regulations, with potential fines for breaches of as much as 6% of global turnover, according to the DSA (Digital Services Act) and between 10% and 20% of global turnover, according to the DMA (Digital Markets Act). The flow of international data will also increase in 2024, particularly transfers between the EU and the United States, by virtue of the new Data Privacy Framework approved in July 2023. We will also see fresh scrutiny from NGOs and digital rights groups to ascertain the legality of these transfers and whether they respect individual privacy.
5. Economic fallout and debt sustainability
The economic consequences of the succession of crises of recent years will be more visible in 2024, especially the impact of the interest rate hikes to counter the biggest spike in inflation in 40 years following the energy crisis of 2022. Meanwhile, tougher financing conditions will limit fiscal policy, following the rapid rise in borrowing to tackle COVID-19 and the impact of the war in Ukraine.
In a climate like this, growth will be slow. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) does not expect inflation to return to the target of most central banks until 2025, which augurs high interest rates for a long time yet, especially if there is a strain on oil prices again against a backdrop of geopolitical uncertainty. The IMF’s growth forecast for 2024 is 2.9%, much the same as the estimate for 2023 and below pre-pandemic growth rates.
Economies, however, will cool unevenly. The United States appears to have dodged recession thanks to the strength of its labour market and of fiscal incentives, which means it is likely to have a softer landing. Industrial relocation policies, like the Inflation Reduction Act, record corporate profits after Covid and the extraordinary loss of purchasing power caused by inflation are some of the ingredients to explain the resurgence of the US labour movement, without precedent since the 1970s. Its success may spread to other sectors and economies with strained labour markets. Thus, a fall in inflation and an increase in salaries in 2024 could provide some economic relief.
In the European Union, there will be greater scrutiny of public accounts, especially those of countries with least financial wiggle room like Italy, following a sharp increase in borrowing to tackle the pandemic and the impact of the war in Ukraine, owing to financing conditions and the entry into force of the reform of the EU’s fiscal rules. “Fiscal discipline” will also loom large in the negotiation of the EU’s new budget framework (MFF), where its greatest wishes (support for Ukraine, backing for industrial policy, the green transition and an increase in appropriations for defence, migration or the Global Gateway) will come face to face with reality (lack of resources or agreement to increase them). The adoption of the European Economic Security Strategy and the outcome of the antidumping investigation into Chinese subsidies on electric vehicles will go a long way to determining whether, on the economic front, the EU opts to align with the United States in its strategic competition with China or tries to be a champion of a reformed globalisation.
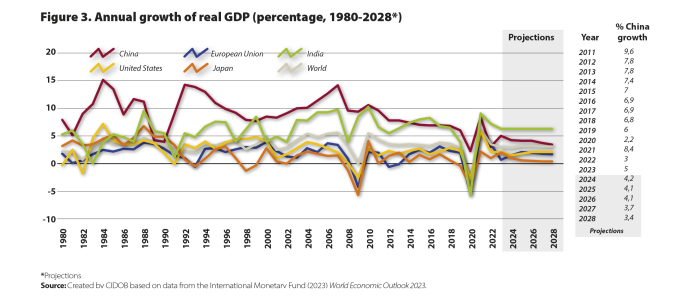
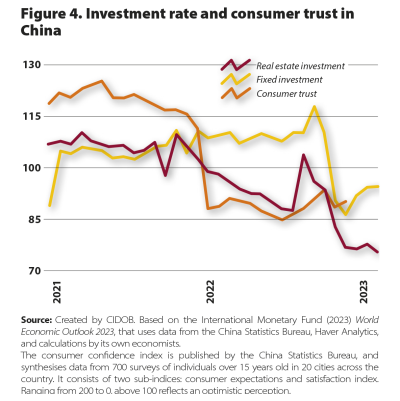
It will also be necessary to keep a close eye on the development of China, which is facing its lowest economic growth in 35 years, not counting the Covid years, weighed down by its imbalances, particularly as far as an excessive accumulation of debt and dependence on the property sector are concerned. The change in the rules of globalisation prompted by US strategic competition will also hamper its exports and capacity to attract capital in a climate in which the Chinese leadership prioritises economic security over growth. With unfavourable demographics, the country has yet to establish domestic consumption as a motor for growth.
Emerging economies will feel the force of China’s slump, especially those with greater trade and financial dependence. The success of the Belt and Road Initiative in terms of investment volume has been overshadowed by repayment difficulties in up to 60% of the loans, which along with criticism has led Xi Jinping to announce a new phase of investments with smaller projects. In 2024, China’s new role as a lender of last resort and its participation in the debt restructuring processes of countries in distress will have growing importance in how it is perceived and in its geoeconomic influence over the Global South.
A large number of emerging countries are in a delicate fiscal situation. In a climate of rapid tightening of financial conditions and a strong dollar, that also exacerbates their external vulnerability. While some countries such as Mexico, Vietnam or Morocco are capitalising on the reconfiguration of trade and value chains (nearshoring), most emerging economies are likely to be adversely affected by a scenario of greater economic fragmentation. According to the WTO, trade in goods between hypothetical geopolitical blocs – based on voting patterns in the United Nations – has grown between 4% and 6% slower than trade within these blocs since the invasion of Ukraine.
In this climate of scant monetary and fiscal space, the buffer for cushioning another crisis is extremely thin, which could exacerbate market volatility and nervousness in the face of episodes of uncertainty. The main focus of attention may shift from Ukraine to the Middle East, since shocks from oil are felt more broadly across the economy than those from natural gas. This could directly affect the EU and Spain, which are particularly dependent because they import over 90% of the oil they consume. In addition, strategic oil reserves in the United States have not been so low since 1983 and the few countries with capacity to increase crude production (Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates and Russia) may not be inclined to do so without significant political concessions.
6. South(s) and North(s)
In our outlook for 2023 we announced the consolidation of the Global South as a space of confrontation and leadership and pointed to the strategic presence of India, Turkey, Saudi Arabia or Brazil. In 2024, this reconfiguration will go a step further. The contradictions and fragmentations of this dichotomous North-South approach will become more apparent than ever. The Global South has established itself as a key actor in the pushback against the West on anti-imperialist grounds or over double standards. The most symbolic image of this moment of geopolitical expansion will come in October 2024, when the BRICS bloc meets in Russia to formalise its expansion. Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa are welcoming Saudi Arabia, Egypt, the United Arab Emirates, Ethiopia and Iran into the fold. Together they account for 46% of the world’s population, 29% of global GDP and include two of the three biggest oil producers in the world. Thus, the BRICS will have an even more powerful voice, although, inevitably, it may also mean more internal contradictions and conflicting agendas. The election of Javier Milei as the president of Argentina, who has confirmed his decision not to join the BRICS, also feeds into the idea of this clash of agendas and interests in the Global South. Saudi Arabia and Iran vie for strategic influence in the Persian Gulf. India and China have their own border disputes in the Himalayas. The Global South will continue to gain clout, but it will also be more heterogeneous. Other than a shared postcolonial rhetoric, its action is extremely diverse.
The Global South is multiregional and multidimensional and comprises different political regimes. But it is also a geographical space where global trade flows are consolidating as a result of reglobalisation. The latest WTO annual report confirms that, while advanced economies are still key players in world trade, they are no longer dominant. However, , if in 2023 we spoke of the geopolitical acceleration of the “others”, with India as the symbol of this potential leadership of the Global South, in 2024 it will be Latin America that tries to take a central role. Brazil will host the G20, while Peru will be the venue for the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) summit.
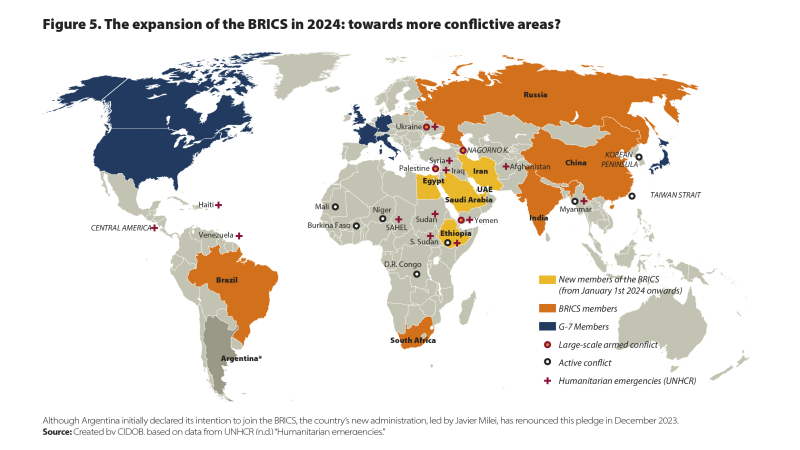
And as we move beyond dichotomies, a deep internal crack may also appear in the Global North should the return of Donald Trump to the White House materialise. Transatlantic distance dominates a new framework of relations that is more transactional than a conventional alliance. Washington and Brussels’ differences will worsen in 2024 when the United States asks the European Union to increase its contributions to the government of Volodymyr Zelensky and internal divisions among the member states prevent it. The second half of 2024 will be particularly tense, when Hungary – the most reluctant EU country when it comes to military aid and Ukraine’s possible accession – takes over the EU’s rotating presidency. It will also be paradoxical if this rift in the Global North widens because of the Ukraine war. Precisely, in 2023, the Ukrainian conflict was the mortar that cemented transatlantic unity, and confronted the EU and the United States with the limits of their ability to influence in the face of a Global South that questioned the double standards of the West. In 2024, however, the war in Ukraine may increase the distance between Washington and Brussels.
Despite this logic of confrontation, the geopolitical short-sightedness of binarism is increasingly misplaced. And yet, it is difficult to overcome. The fact that both the United States and the European Union conceive their relations with Latin America solely as a space for resource exploitation and geopolitical dispute with China, is part of that short-sightedness. For the moment, the repeated failure of the negotiations over an EU-Mercosur agreement are dashing South America’s hopes of being able to boost its trade presence in the European single market. Talks will resume in the first half of 2024, after Paraguay takes over the Mercosur presidency from Brazil.
7. Backsliding on international commitments
The year 2023 left international cooperation in a shambles. Employing increasingly blunt language, António Guterres declared that the world is “woefully off-track” in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which reached the halfway point to their 2030 deadline in 2023. The coming year must prove whether the international community is still capable of and wishes to agree on coordinated responses to common global problems through organs of collective governance. It will not be easy. We face an acceleration of the ecological crisis, record migration and forced displacements and a clear regression of the gender equality agenda.
For the first time, the International Energy Agency (IEA) is projecting that global demand for oil, coal and natural gas will reach a high point this decade, based only on current policy settings, according to the World Energy Outlook 2023. In the short term, fossil fuel-producing countries are ignoring the climate warnings and plan to increase the extraction of coal, oil and gas. The choice of an oil state, the United Arab Emirates, as the host of a climate summit and the appointment of a fossil fuels executive as president was a bad omen at the very least.
And yet, COP28 in Dubai has been the first to have managed to produce a text that explicitly recognizes the need to "transitioning away from" fossil fuels: oil, coal and gas, as the main culprits of the climate crisis. Although the final agreement has been celebrated as historic for referring to this need to initiate a transition to guarantee net zero emissions in 2050, the degree of ambition demonstrated is not sufficient to meet the objectives of the Paris Agreement. Likewise, while the creation of a Loss and Damage Fund to compensate the countries most affected by climate change is also a positive step, the initial collection of $700 million falls far short of what is necessary. Every year developing countries face $400 billion in losses linked to climate action.
In this context, not only do we run the risk of exacerbating climate impacts; we shall also see a rise – more acutely than ever – of social and political tensions between governments and societies over the exploitation of resources. In Europe there is growing discontent with the EU’s climate transition policies and the rise of Eurosceptic and radical right forces in the European Parliament elections of June 2024 will raise this pressure still further. The flurry of regulatory activity on climate and industrial matters is increasing the politicisation of this issue and stoking social unrest in certain member states. Italy, Poland, the Netherlands and certain sectors in Germany, particularly the far-right Alternative for Germany (AfD), are trying to limit the EU’s ambitions on climate action. The arrival of a new government in Sweden, backed by the radical right, has slammed the brakes on the climate commitments led by one of the countries that has most contributed to EU environment policies. A hypothetical return of Donald Trump to the White House would also shake again some of the limited domestic and international progress in this area.
According to a poll carried out by Ipsos, while a large part of European households continues to put the environment before economic growth, this proportion is declining. If in 2019, 53% of households preferred to protect the environment, in 2022 the figure had fallen by 5 percentage points, despite the clear impact of climate phenomena. Yet the trend of “not in my back yard” is not limited to Europe. In late 2023, we saw the resistance of Panamanians against a mining contract extension. Some experts speak of a “clash of environmentalisms” to refer to the confrontation that arises between those who wish to protect their country’s natural resources and do not want to see a deterioration in their ecosystems and the interests of governments seeking resources to fuel their energy transition. We might see the same in the European Union. In early 2024, the Critical Raw Minerals Act will enter into force. It aims to guarantee the supply of nickel, lithium, magnesium and other essential materials for the green transition and strategic industries that are vital for electric cars and renewable energies, military equipment and aerospace systems, as well as for computers and mobile phones. And with this in mind the EU means to revive the mining industry on the continent. It is a move that may trigger protests by ecologists in the EU in the coming months.
UN member states are also expected to reach a global agreement to end plastic pollution in 2024. It will be an international legally binding treaty and is hailed as the most important multilateral environmental pact since the Paris Agreement, setting a plan of action to 2040.
However, it is gender policies and migration policies that are most exposed to this radical wave that has transformed government agendas, particularly in the European Union and Latin America. While it is true that gender parity recovered to pre-pandemic levels in 2023, the rate of progress has slowed. At the present pace, it will take 131 years to reach full parity. Although the share of women hired for positions of leadership has increased steadily by approximately 1% a year globally over the last eight years, that trend was reversed in 2023, falling to 2021 levels.
The emerging feminist foreign policies, which defined those countries with a clear commitment to promoting gender equality in international relations, have added four important losses in recent months: Sweden, Luxembourg, The Netherlands, and Argentina. The changes in government, together with the growing politicization and polarization of issues perceived as "feminist", have demonstrated the easy abandonment of these initiatives, dependent on the progressive orientations of the governments in power. Mexico, another of the countries that has adopted these policies, will face elections in June that will also mark the continuity or abandonment of its commitment to gender equality in foreign action. And, despite not having a feminist foreign policy, Trump's return to the White House could lead to the reinstatement of restrictive abortion policies and funding cuts against international NGOs that promote sexual and reproductive rights.
Moreover, the International Institute for Democracy and Electoral Assistance (International IDEA) reports a resurgence of anti-feminist trends in countries like Croatia and Italy and notes sexist and homophobic speech on the part of European leaders such as Viktor Orbán, Andrzej Duda or Giorgia Meloni, who have justified attacks on women’s and LGBTQIA+ rights, undermining years of efforts to secure progress in breaking up gender stereotypes. Although the EU Gender Action Plan III is valid until 2025, a change in Brussels would also dilute the commitments of one of the actors most involved in this area.
On a more positive note, it will be interesting to follow, in 2024, the progress of the Convention against Crimes against Humanity, which the UN is developing, as feminist and civil society movements around the world will take this opportunity to try to codify the gender apartheid as a crime against humanity – especially due to the Taliban regime's continued discrimination and oppression of Afghan women, and the situation of Iranian women.
European migration policies have also suffered a major setback. The EU Pact on Migration and Asylum, which is set to move forward before the European elections in 2024, is a legitimisation of the EU’s anti-immigration policies. The deal allows delays in registering asylum seekers, the introduction of second-rate border asylum procedures and extends detention time at the border. In short, it lowers standards and legalises what hitherto was unequivocally illegal.
This looming agreement reflects the levels of polarisation and politicisation that set the tone of the European response to migration. And as we enter the run-up to the election campaign the migration debate will be even further to the fore in the coming months. It is, what’s more, part of another, deeper process. The EU’s externalisation policies have also fostered the stigmatisation of immigrants and refugees in the MENA region (Middle East and North Africa).
8. Humanitarian collapse
War and violence drove forced displacement worldwide to a new high estimated at 114 million people by the end of September 2023, according to UNHCR. The main drivers of these forced displacements were the war in Ukraine and conflicts in Sudan, the Democratic Republic of Congo and Myanmar, as well as drought, floods and insecurity blighting Somalia and a prolonged humanitarian crisis in Afghanistan.
In the first six months of 2023 alone, 1.6 million new individual asylum applications were made, the highest figure ever recorded. This is not an exceptional situation. The reignition of forgotten conflicts has increased levels of volatility and violence. In October 2023, over 100,500 people, more than 80% of the estimated 120,000 inhabitants of Nagorno-Karabakh, fled to Armenia after Azerbaijan took control of the enclave. There were also thousands of displaced persons in northern Shan because of an escalation in fighting between the Myanmar armed forces and various armed groups. At the end of October 2023, nearly 2 million people were internally displaced in Myanmar, living in precarious conditions and in need of vital assistance. And the images of over 1 million Palestinians fleeing their homes because of the Israeli military offensive, after Hamas attack from October 7, illustrate the humanitarian crisis afflicting Gaza.
This increase in the number of displaced persons and refugees, however, has not been accompanied by a boost in international aid. Close to 1 million Rohingya refugees in Bangladesh must cope with declining international commitment. The United Nations reduced its food assistance and humanitarian aid to this group by one third in 2023. A lack of international funding considerably reduced assistance levels in 2023 and the World Food Programme was obliged to cut the size and scope of its food, monetary and nutritional assistance by between 30% and 50%. Some 2.3 billion people, nearly 30% of the global population, currently face a situation of moderate or severe food insecurity. Further rises in food prices in 2024 and the impact of adverse weather conditions on agricultural production may make the situation even worse still. The United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) anticipates that a total of 105 to 110 million people will require food assistance at least until early 2024, with an increase in need in the regions of southern Africa and Latin America and the Caribbean, and a net decrease in eastern Africa.
Experts are pointing to the risk of a new rice crisis in 2024, as a result of India’s export restrictions to try to cushion the effects of a drop in domestic production. The shock wave from the ban has also driven up the price of rice in Thailand and Vietnam, the second and third biggest exporters after India, which have seen prices rise by 14% and 22%, respectively. Added to that are the effects of the climate phenomenon known as El Niño, associated with heat and drought across the Pacific Ocean, which could harm production in 2024. Experts are currently warning that if India maintains the current restrictions, the world is headed for a repeat of the rice crisis of 2008.
El Niño, which is set to continue to mid-2024, is usually associated with increased rainfall in certain areas of southern South America and the southern United States, the Horn of Africa and Central Asia. On the other hand, El Niño can also cause severe drought in Australia, Indonesia and parts of Southeast Asia.The last episode of the phenomenon, in 2016, was the warmest year on record, with global heat records that have yet to be surpassed.
Donor governments and humanitarian agencies must prepare for major assistance needs in multiple regions. The year 2023 has left us some indication of it: extreme drought in the Amazon and maritime traffic restrictions in the Panama Canal; forest fires in Bolivia and power cuts in Ecuador owing to low electricity production in over 80% of hydroelectric plants; the worst floods on record in northwest Argentina, which also caused landslides affecting over 6,000 people; and a devastating category 5 hurricane in Mexico that surprised the authorities and scientists, who failed to foresee the intensity of the phenomenon.
9. Securitisation vs. rights
The conflict between security and fundamental rights has been a constant feature of 2023 and the electoral uncertainty of the coming months will only compound the urge to pursue heavy-handed policies and control. The public debate throughout Latin America, without exception, has been dominated by security, directly impacting other crises such as migration, which has affected the entire continent for a decade and in 2024 is expected to be even more intense. “Bukelism” has a growing number of fans. The new Argentine president, Javier Milei, has said he is an admirer of the hard-line polices of the Salvadoran president, Nayib Bukele. The election campaign in Ecuador was also coloured by the debate on security.
The continent is fighting a new crime wave that has spilled into traditionally more stable countries that are now part of lucrative drug-trafficking routes, as is the case of Paraguay and Argentina. People trafficking, particularly the criminal exploitation of the Venezuelan migration crisis, has also grown throughout Latin America. Against this backdrop, the United Nations and Interpol have launched a joint initiative to combat human trafficking. It remains to be seen what impact the Venezuelan elections might have on this migration crisis, which has already led to over 7 million people leaving their homes since 2014.
Moreover, increasing impunity has also brought a mounting risk of authoritarian inclinations on the part of governments in Latin America, with the militarisation of public security and an undermining of democracy across the continent. In the European Union too. For some time, the sense of vulnerability has been a political boon for certain forces in the EU. With the outbreak of war in Gaza, some European countries ramped up security for fear of terrorist attacks, going to the extreme of banning demonstrations in support of the Palestinian people, as in France. In this climate, the securitisation of social movements is also emerging as a strategy that will continue to gain prominence in 2024. More and more, democratic governments are stepping up the pressure on protest movements: fines, curbs on free speech or judicial persecution are shrinking the space for civil dissent. On this point, the EU has reached an agreement to legislate against strategic lawsuits that seek to discourage public participation or silence independent media (known as SLAPPs) which is set to be ratified before the end of the current legislative term.
Finally, the debate on security and its impact on individual rights will also mark the months leading up to the 2024 Olympic Games in Paris. Civil rights groups have decried the French government’s plans to use AI surveillance cameras to pick up real-time activity on the streets of the capital during the games. Technology is a crucial component of the transformation that security and conflict are undergoing. Drones have become a vital weapon for the resistance in Ukraine, and in the arsenal of Hamas in its October 7th attack on Israel. A United States in the midst of budget cuts is, however, poised to inject extra cash into the Pentagon in 2024 for the development of “electronic warfare” programmes.
10. The decoupling of interests and values
There is a common thread in many of the previous points that connects an increasingly diverse and (dis)organised world through changing interests and alliances. In its 2023 Strategic Foresight Report, the European Commission acknowledges that the “battle of narratives” it used for so long as an argument in the geopolitical confrontation between democracy and authoritarianism is becoming obsolete. It goes further than the realisation that the West has lost the battle for the narrative in the Ukraine war and that its double standards in the face of global conflicts diminishes the EU’s clout. Sudan is the clearest example of how the West can commit to wars it considers existential for the survival of its own values, such as the Ukraine one, while it ignores the genocide being carried out, with house-to-house murders, in the refugee camps of Darfur.
The world has turned into a “battle of offers”, shaping both public opinion and government action. There is a growing diversity of options and alliances. Thus far, hegemonic narratives are either challenged or no longer serve to make sense of the world. In this “unbalanced multipolarity”, with medium-sized powers setting regional agendas, the major traditional powers are compelled to seek their own space. Global competition for resources to fuel the green and digital transitions accentuates this variable geometry of agreements and alliances still further. And the results of the series of elections in 2024 may ultimately reinforce this transformation. The United States’ isolationist inclinations are real. Vladimir Putin will confirm his resilience at the polls, after dodging the effects of the international sanctions and building an economic apparatus to withstand a long war in Ukraine. In India, Narendra Modi’s popularity remains intact and drives the dominance of his party. The election question sets the stage for a 2024 that begins wide open. The crisis of the liberal order, aggravated by the international reaction to the latest conflicts, and the erosion of multilateralism – with an explicit challenge to the United Nations – foster yet further this sensation of a dispersion of global power towards an assortment of dynamic medium-sized powers capable of helping to shape the international environment in the coming decades.
A pivotal year begins to evaluate the resistance capacity of democratic systems long subdued to a profound erosion. We will be attentive to the outcome of the ballots and to the increasing unabashed actions of bullets, pressing the limits of impunity.

CIDOB calendar 2024: 75 dates to mark on the agenda
January 1 – Changeover in the United Nations Security Council. Algeria, Guyana, the Republic of South Korea, Sierra Leone and Slovenia start their terms as non-permanent members of the UN Security Council, replacing Albania, Brazil, Gabon, Ghana and the United Arab Emirates, whose terms end.
January 1 – Dissolution of the Republic of Artsakh. The self-proclaimed Republic of Nagorno-Karabakh will cease to exist at the start of the year, after more than three decades of control over the territory. In September 2023, Azerbaijan launched a military offensive to reintegrate this predominantly ethnic Armenian-populated enclave. The assault led the self-declared republic to announce its dissolution.
January 1 – BRICS expansion. Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates will join Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa as full members of BRICS. Argentina’s new president, Javier Milei, has finally ruled out his country's incorporation.
January 1 – Belgian presidency of the Council of the European Union. Belgium takes over the rotating presidency of the Council from Spain, marking the end of this institutional cycle. The Belgian semester will hold until June 30.
January 7 – Parliamentary elections in Bangladesh. The vote will take place against a backdrop of deep political division in the country. This division led to mass demonstrations by the opposition at the end of 2023, calling for an interim government to oversee the elections. The current prime minister, Sheikh Hasina Wazed, is looking to for another term after 15 years in power, while her main rival and leader of the Bangladesh Nationalist Party, Khaleda Zia, is currently under house arrest on charges of corruption.
January 13 – General elections in Taiwan. For the first time since Taiwan became a democracy, three candidates are competing for the presidency after the opposition failed to form a common front: the current vice president Lai Ching-te, from the ruling Democratic Progressive Party; Hou You-yi from the Kuomintang, and Ko Wen-je, a former mayor of Taipei and leader of the Taiwan People’s Party. The outcome of these elections will mark the course of Taiwan’s policy towards China, with an eye on the United States, at a time of growing tension between Taipei and Beijing.
January 14 – Inauguration of Bernardo Arévalo as president of Guatemala. To widespread surprise, the Seed Movement candidate won the 2023 elections. Since the vote was held, political and social tension in the country has been rising due to efforts by the Guatemalan public prosecutor’s office to overturn the election results and prevent Arévalo from taking office.
January 15-19 – World Economic Forum. An annual event that gathers major political leaders, senior executives from the world’s leading companies, heads of international organisations and NGOs, and prominent cultural and social figures. This year’s meeting will mainly focus on examining the opportunities provided by the development of emerging technologies and their impact on decision-making and international cooperation.
January 15-20 – 19th Summit of the Non-Aligned Movement. Uganda will be the venue for the next summit of the 120 countries that make up this grouping of states. The theme for this edition is “Deepening cooperation for shared global affluence” and it is scheduled to tackle multiple global challenges of today with a view to fostering cooperation among the member states.
January 21-23 – Third South Summit of G-77 + China. Uganda will host this forum looking to promote South-South cooperation, under the theme “Leaving no one behind”. The 134 member states from Asia, Africa, Latin America and the Caribbean will focus on the areas of trade, investment, sustainable development, climate change and poverty eradication.
February 4 – Presidential elections in El Salvador. Nayib Bukele, who heads the New Ideas party and currently holds the presidency of El Salvador, is shaping up as the clear favourite for re-election. The country has been in a state of emergency since March 2022, in response to the security challenges affecting the nation.
February 8 – Presidential elections in Pakistan. Since Imran Khan’s removal as prime minister in April 2022, Pakistan has been mired in political instability, deep economic crisis and rising violence on the part of armed groups. The elections will be supervised by a caretaker government after the expiry of the Pakistani parliament’s five-year term in August 2023.
February 14 – Presidential and legislative elections in Indonesia. Three candidates are competing to succeed the current president, Joko Widodo, who after two terms cannot stand for re-election. The next leader will face the challenges of boosting growth in an economy reliant on domestic consumption, driving the development of the tech industry and navigating pressure from China and the United States to protect their national interests.
February 16-18 – 60th Munich Security Conference. Held every year, it is the leading independent forum on international security policy and gathers high-level figures from over 70 countries. Strengthening the rules-based international order, the impact of the wars in Ukraine and Gaza, resisting revisionist tendencies or the security implications of climate change will be some of the main issues on this year’s agenda.
February 17-18 – African Union Summit. Ethiopia, which holds the presidency of the African Union, will be organising the summit. This year, it will address some of the numerous issues in Africa, including instability in the Sahel, growing global food insecurity, natural disasters on the continent or democratic backsliding. In addition, the tensions between Morocco and Algeria will be centre stage as both countries are vying for the presidency.
February 25 – Presidential elections in Senegal. Following multiple waves of protests, the current president, Macky Sall, announced he would not be standing for a third term. It is the first time in the country’s democratic history that a sitting president will not be standing in the elections. The need to ensure jobs for the country’s young population will be one of the key issues in the election campaign.
February 26-29 – Mobile World Congress. Barcelona hosts the world’s biggest mobile phone event, gathering the leading international tech and communications companies. This edition will be devoted to 5G technology, connectivity, the promotion of human-centred artificial intelligence or the digital transformation, among other themes.
March 1 – Parliamentary elections in Iran. With an eye on the succession of the ageing Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, Iranians will elect their representatives to the Islamic Consultative Assembly and the Assembly of Experts, the latter body in charge of electing the new supreme leader in the coming years. The elections will be marked by the escalation of tension in the Middle East and the deep economic and social crisis that has increased popular disaffection with the regime.
March 8 – International Women’s Day. Now a key date on the political and social calendar of many countries. Mass demonstrations have gained momentum in recent years, particularly in Latin America, the United States and Europe. The common goal is the struggle for women’s rights and gender equality throughout the world.
March 10 – Parliamentary elections in Portugal. The country faces a snap election after the institutional crisis triggered by the resignation of the socialist prime minister, António Costa. The former leader was the target of a judicial investigation over alleged corruption that directly involved several members of his government team.
March 15-17 – Presidential elections in Russia. While Vladimir Putin is expected to secure re-election, maintaining his grip on power until 2030, Russia will go to the polls against a backdrop of multiple domestic security challenges. The Russian withdrawal from the Ukrainian region of Kharkiv, the impact of the war in Ukraine, the failed Wagner uprising of June 2023 and the antisemitic disturbances in the North Caucus in October could force Putin to use the election calendar to embark on major a shakeup of the political and military leaderships.
March 18 – 10th anniversary of Russia’s annexation of Crimea. The annexation of Crimea by Russia, which had invaded the region some weeks earlier, was formalised via a referendum on Crimea’s political status that went ahead without international recognition. The event took place following the fall of the then Ukrainian president, Viktor Yanukovych, a pro-Russian, in the wake of a series of protests with a clear pro-European bent.
March 21-22 – Nuclear Energy Summit. The International Atomic Energy Agency and the Belgian government will gather over 30 heads of state and government from across the world, as well as energy industry and civil society representatives. The summit seeks to promote nuclear energy in the face of the challenges posed by reducing the use of fossil fuels, enhance energy security and boost sustainable economic development.
March 31 – Presidential elections in Ukraine. According to the Ukrainian constitution, presidential elections must be held on the last Sunday in March of the fifth year of the presidential term of office. However, it is uncertain whether they will go ahead given they are illegal under martial law, in effect since the start of Russia’s invasion of the country in 2022. A lack of funds and the Ukrainian people’s opposition to holding elections in wartime are important factors.
March 31 – Local elections in Turkey. The Republican People’s Party (CHP), the main opposition, is hoping to maintain control of the key municipalities it won in 2019. They include the capital, Ankara, Istanbul and other major cities. Recep Tayyip Erdoğan’s re-election and the retention of the parliamentary majority in the elections of 2023 have prompted his Justice and Development Party (AK Party) to try to make up ground at municipal level.
April 7 – 30th anniversary of the genocide in Rwanda. The deaths of the presidents of Burundi and Rwanda in a plane crash provided the trigger for a campaign of organised and systematic extermination of members of the Tutsi population at the hands of Hutu extremists that would last 100 days. On July 15th, 1994, the Rwandan Patriotic Front established a transitional government of national unity in Kigali that would put an end to the genocide. Between 500,000 and 1 million people are estimated to have been murdered.
April-May – General elections in India. Despite growing illiberal tendencies, the “world’s biggest democracy” goes to the polls in April and May. The current prime minister, Narendra Modi, is aiming for a third term against an opposition that is more united than ever under the Indian National Development Inclusive Alliance (INDIA).
May 2 – Local elections in the United Kingdom. Elections will take place for local councils and mayors in England, including London and the combined authority of Greater Manchester. The elections will be seen as an indicator of the level of support both for the Labour Party and for the Conservatives ahead of general elections scheduled for January 2025.
May 5 – General elections in Panama. Panamanian society will elect new representatives for the presidency, National Assembly, mayoralty and other local representatives. The elections will take place against a backdrop of marked polarisation and rising social tension, exacerbated by issues relating to domestic security, political disputes and the management of natural resources.
May 19 – Presidential and legislative elections in the Dominican Republic. The current president, Luis Abinader, leader of the Modern Revolutionary Party, is seeking re-election in a vote in which most opposition parties will unite under the Opposition Alliance Rescue RD. Territorial, migration and economic tensions with neighbouring Haiti will be central issues during the election campaign.
June – Presidential elections in Mauritania. The current president, Mohamed Ould Ghazouani, will seek re-election after four years of business as usual following the departure in 2019 of the former president, Mohamed Ould Abdel Aziz, who today faces multiple corruption charges. The winner of the elections will have to deal with rising social tension, as well as geopolitical tensions across the region.
June 2 – General and federal elections in Mexico. Claudia Sheinbaum, the official shortlisted presidential candidate for the National Regeneration Movement (Morena), is the clear favourite against the main opposition candidate from the Broad Front for Mexico, formed by the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI), National Action Party (PAN) and the Party of the Democratic Revolution (PRD). Voters will not only elect the president and the government, but also senators and federal deputies, as well as thousands of state and/or municipal officials in 30 of the 32 federal entities.
June 6-9 – Elections to the European Parliament. Voting will take place simultaneously in the 27 countries that form the European Union. Some of the major questions are how far populist and far-right parties will advance, how much clout the traditional social democrat and conservative families will wield and the possible alliances that might form for the subsequent selection of key European posts.
June 9 – Federal elections in Belgium. Coinciding with the Belgian presidency of the European Union, the country will hold federal, European and regional elections on the same day. One of the most significant issues will be how well the far-right party Vlaams Belang fares. It is aiming for a considerable increase in its support to test the resistance of the cordon sanitaire that has excluded it from power until now.
June 13-15 – 50th G-7 summit in Italy. Savelletri, a small town in the Italian region of Puglia, will be the venue for a new meeting of the G7. The summit will tackle the main geopolitical challenges on the global stage and their impact on the international economy, along with other crucial issues on Italy’s agenda, such as immigration and relations with Africa.
June 20 – World Refugee Day. The number of forcibly displaced people hit all-time highs in 2023. There are refugees and internally displaced persons due to the impact of the war in Ukraine and the numerous conflicts in the Middle East and Africa, as well as the impacts of climate change. During that week in June, the UNHCR will release its annual report on the global trends in forced displacement.
First half of 2024 – Deployment of an international mission to Haiti. Kenya will lead the deployment of a security contingent with the participation of other countries. The goal is to tackle the gang violence in Haiti that is causing a major security and governance crisis. In October 2023, following a request from the secretary general and Haitian prime minister, the United Nations Security Council authorised a multinational security support mission for a period of one year.
First half of 2024 – Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad) Summit. India will host a new meeting of this strategic forum for the Indo-Pacific region formed by Australia, India, Japan and the United States to address common issues regarding trade, critical technologies, human rights and climate change.
July – 24th Summit of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation. Kazakhstan holds the yearly rotating chairmanship of the main regional forum in Central Asia for security, economic and political affairs, made up of China, India, Iran, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Pakistan, Russia, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. The priorities of the Kazakh chairmanship focus on matters of security and regional unity, as well as economic development and regional trade. Belarus is expected to join the organisation this year.
July 1 – Hungary takes over the rotating presidency of the Council of the European Union. Hungary will take over the rotating presidency of the Council of the European Union in the second half of the year, amid tension with the European Commission and Parliament over its failures to comply with EU law.
July 8-18 – High-Level Political Forum on Sustainable Development. World leaders and representatives will meet in New York to follow up and review the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), as well as present Voluntary National Reviews on the SDGs. The theme will be “Reinforcing the 2030 Agenda and eradicating poverty in times of multiple crises: the effective delivery of sustainable, resilient and innovative solutions”.
July 9-11 – NATO Summit. Washington will be the venue for the NATO summit, where the presentation of a security strategy for the southern flank is expected, in response to the mandate arising out of the Vilnius summit in 2023. In addition, 2024 marks the 75th anniversary of the founding of NATO.
July 26-August 11 – Summer Olympic Games in Paris. France will host the Games of the XXXIII Olympiad, the world’s main sporting event, which is held every four years. It affords the hosts a good opportunity to kick-start an economy that has stagnated in recent years.
August – Presidential and parliamentary elections in Rwanda. The incumbent president of Rwanda, Paul Kagame, who has been in the post since 2000, is running for re-election after three successive ballots in which he has polled over 90% of the votes.
September – Parliamentary elections in Austria. The burning question is whether the conservatives (ÖVP) and the greens (Die Grünen) will be able to repeat their current government coalition or whether the results of the populist Freedom Party of Austria (FPÖ) and the social democrats of the SPÖ will offer alternative majorities.
September 22-23 – UN Summit of the Future. Based on the “Our Common Agenda” report presented by UN Secretary General António Guterres in 2021, on multilateralism and international cooperation, this high-level event aims to accelerate the fulfilment of existing international commitments and tackle emerging challenges and opportunities. The culmination of this effort will be the creation of a Pact for the Future negotiated and endorsed by the participating countries.
September 24 – General Debate of the 79th Session of the United Nations General Assembly. A yearly event that brings together the world’s leaders to assess the current state of their national policies and their world views.
September 26-27 – 10th anniversary of the Ayotzinapa case. Mexico will mark the 10th anniversary of the Ayotzinapa (or Iguala) case, one of the biggest human rights scandals in the country’s recent history. Still unsolved, the case involved the forced disappearance of 43 students from the Ayotzinapa Rural Teachers’ College, Guerrero state.
October – 16th BRICS Summit. Kazan in Russia will be the venue for the summit of the new BRICS, now expanded to 11 countries, adding impetus to Moscow’s efforts to demonstrate that the country is not isolated despite the large-scale invasion of Ukraine.
October 1 – 75th anniversary of the founding of the People’s Republic of China. It is 75 years since Mao Zedong founded the People’s Republic of China. The event marked the end of the civil war between the Chinese Communist Party and the Kuomintang that had broken out immediately after the surrender of Japan and the dissolution of the Second United Front between the two political forces during the Second Sino-Japanese War.
October 6 – Municipal elections in Brazil. The elections will be a good gauge of the level of support for the Workers’ Party and the parties that back President Lula, as well as of the advance, or otherwise, of Bolsonaro-linked candidates. In the cities where a second round of voting is required, it will take place on October 27.
October 9 – General and regional elections in Mozambique. President Filipe Nyusi will end his second and final presidential term. According to the country’s constitution, he cannot stand again. His party, the Liberation Front of Mozambique (FRELIMO), which has been in power for decades, must find another candidate. The next government will face various challenges, including political tension, an increase in jihadi terrorism and marked social exclusion.
October 24 – International Day of Climate Action. The goal is to mobilise and raise awareness of the effects of climate change among society and governments across the world. It is a good moment to analyse the different agendas to fight climate change and the progress being made in the most polluting countries.
October 27 – General elections in Uruguay. The Broad Front (FA), a centre-left party with strong ties to the trade unions and other social organisations, will compete for victory against the centre-right Multicolour Coalition, which is currently in power and has faced several corruption cases in recent months.
November – APEC Summit. Peru will host a new meeting of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation forum, which gathers 21 countries. The theme this year is “People. Business. Prosperity”.
November – COP29 Climate Change Conference. Azerbaijan will host the world's largest international summit dedicated to climate change in 2024. For the second consecutive year, it will be held in a country whose economy is dependent on fossil fuel production.
November – 29th Ibero-American Summit. Ecuador will host the Ibero-American Summit of heads of state and government under the theme “Innovation, inclusion and sustainability”. In parallel, the main cities of Latin America, Spain and Portugal will hold a “Meeting of Ibero-American Cities”, the conclusions of which will be presented during the summit.
November 4-8 – 12th World Urban Forum. Cairo will host the premier gathering on urban issues and human settlements organised by UN-Habitat.
November 5 – Presidential elections in the United States. The incumbent president, Joe Biden, is seeking re-election and, with the former president, Donald Trump, still to be confirmed as the Republican presidential nominee, the campaign promises to be highly polarised. The election calendar will influence Washington’s foreign policy decisions.
November 5 – General elections in Georgia. The ruling coalition Georgian Dream is looking for yet another term. The war in Ukraine has split the country again between those who seek deeper integration with the West and hope to join the European Union in the future and those who advocate normalising relations with Russia.
November 11 – 20th anniversary of the death of Yasser Arafat. The historic Palestinian leader and president of the Palestinian National Authority died 20 years ago in Paris. He played a crucial role in the Middle East peace process, which, along with Israeli leaders Yitzhak Rabin and Shimon Peres, earned him the Nobel Peace Prize in 1994.
November 18-19 – G-20 summit in Brazil. Under the theme “Building a just world and sustainable planet”, the main topics for discussion and debate at this meeting will include energy transition and development, reform of the global governance institutions, and the fight against inequality, hunger and poverty.
December – Presidential elections in Algeria. President Abdelmadjid Tebboune is expected to run for re-election. The country faces several security challenges due to the instability in the Sahel and the rising tension with Morocco over the Western Sahara. It also plays a crucial role as a supplier of gas to Europe amid the energy crisis caused by the war in Ukraine.
December – General elections in South Sudan. The terms of the peace agreement of 2018, which put an end to an internal armed conflict lasting five years, established the forming of a government of national unity led by the current president, Salva Kiir, and his rival, the vice president, Riek Machar. Kiir has proposed holding free presidential elections in late 2024.
December 7 – Presidential elections in Ghana. The elections are expected to be a two-horse race between Mahamudu Bawumia, the current vice president of the ruling New Patriotic Party (NPP), and the former president, John Dramani Mahama, the candidate of the main opposition party, the National Democratic Congress (NDC). The country is facing its worst economic crisis of recent decades and major security challenges because of the geopolitical situation in the Sahel.
Second half of 2024 – Presidential elections in Venezuela. The Chavistas and the opposition gathered under the umbrella of the Unitary Platform reached an agreement in Barbados on staging presidential elections that provides for the invitation of regional and international observers. The decision came as the United States announced the lifting of sanctions on Venezuelan gas and oil in October 2023.
Pending – 53rd Pacific Islands Forum. Tonga is to host a new meeting of the main discussion forum spanning the region of Oceania, which brings together the interests of 18 states and territories on matters of climate change, the sustainable use of maritime resources, security and regional cooperation. It is a geographical space of growing interest to China and the United States, which have begun a diplomatic race to draw some of these countries and territories into their spheres of influence.
Pending – 44th ASEAN Summit. Laos will host a new meeting of Southeast Asia’s main regional forum, which brings together 10 countries. The theme this time is “Enhancing connectivity and resilience”.
Pending – AI Safety Summit. France will host the second meeting of this international summit whose goal is to foster work and initiatives to tackle the risks posed by artificial intelligence. The first event, held in London in 2023, resulted in the Bletchley Declaration, which advocated greater international cooperation to address the challenges and risks associated with artificial intelligence.
Pending – 33rd Arab League Summit. Bahrein will host a fresh meeting of the main political organisation gathering the countries of the Middle East and North Africa. The Israeli-Palestinian conflict, food and energy security issues, and the regional impacts of the war in Ukraine will be some of the main topics of discussion and debate.
Pending – Presidential and parliamentary elections in Sri Lanka. The social tension in the country, mired in a deep economic crisis that has led to an International Monetary Fund rescue, has increased in recent months and is expected to intensify throughout the electoral process.
Pending – General elections in Chad. Chad’s transitional president, Mahamat Idriss Déby, who came to power in April 2021 via a military junta following the death of his father, Idriss Déby, promised the staging of free elections in late 2024. The country is facing a serious food and security crisis.
Pending – 3rd Summit for Democracy. South Korea will be the host of this US-promoted summit, which since 2021 has gathered heads of government and leaders from civil society and the private sector. Its goal is to address the challenges and opportunities facing democracies in the 21st century on matters relating to democratic governance, safeguarding human rights and fighting corruption.
Pending – General and regional elections in South Africa. The African National Congress (ANC), in power since the first free and general elections in 1994, is looking to stay there, although the main opposition party, the Democratic Alliance, could pull off a surprise. The country faces countless challenges, particularly in matters of security thanks to soaring crime rates, a major energy crisis and high unemployment.
Pending – Presidential elections in Tunisia. They will be the first elections since the power grab by the Tunisian president, Kaïs Saied, in 2021 and the return to authoritarianism of the only country that appeared to have consolidated democracy following the Arab Spring of 2010-2011. Saied has already announced he will not allow the presence of international election observers.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24241/NotesInt.2023/299/en
All the publications express the opinions of their individual authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of CIDOB as an institution